Glossary¶
The glossary provides a short definition of the most common terms, and provides links to the related entries.
Board¶
There are two kinds of boards:
-
The main controller board is powered by a microcontroller or a microprocessor;
-
The extension board drives the e-paper display. PDLS supports the EXT3 and EXT3-1 extension boards.
See also
Check mode¶
The check mode sets how an element reacts to touch and raises the corresponding event.
Three modes are available: normal, instant and direct.
The state of the GUI element needs to be enabled.
See also
Direct check, Enabled state, Instant check, Normal check, Special check
Colours¶
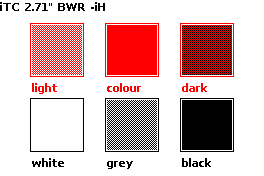
The monochrome e-paper screens provide two basic colours: black and white.
Combining those two basic colours gives one additional shade, totalling three colours.
-
white: basic colour;
-
black: basic colour;
-
grey: combined colour, one dot black, another dot white.
The black-white-red colour e-paper screens provide three basic colours. Combining those three basic colours gives two additional shades, totalling six colours.
-
white: basic colour;
-
black: basic colour;
-
red: basic colour.
and
-
grey: combined colour, one pixel black, another pixel white;
-
light red: combined colour, one pixel red, another pixel white;
-
dark red: combined colour, one pixel red, another pixel black.
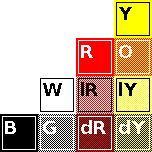
The black-white-red-yellow colour e-paper screens provide four basic colours. Combining those four basic colours gives six additional shades, totalling ten colours.
-
white: basic colour;
-
black: basic colour;
-
red: basic colour;
-
yellow: basic colour;
and
-
grey: combined colour, one pixel black, another pixel white;
-
light red: combined colour, one pixel red, another pixel white;
-
dark red: combined colour, one pixel red, another pixel black;
-
light yellow: combined colour, one pixel yellow, another pixel white;
-
dark yellow: combined colour, one pixel yellow, another pixel black;
-
orange: combined colour, one pixel red, another pixel yellow.
Coordinates¶
Two systems are available:
-
Rectangular coordinates define the top-left and bottom-right points;
-
Vector coordinates define the top-left point and a distance.
See also
Delegated update¶
Normally, the main code commands the refresh of the screen.
With the delegated update option, the elements can trigger the refresh of the screen, with the fast update mode. This allows a more fluid interface, especially for the GUI library.
Warning
The partial update mode is now deprecated. The fast update mode is used instead.
See also
Direct check¶
Default mode is normal check mode.
In direct check mode, the GUI element raises the event when the finger is released from the element. A simplified cinematic sequence is performed.
The mode is recommended when the button triggers the display of a new page.
It requires the state of the GUI element to be enabled.
See also
Enabled state, Check mode, Instant check, Normal check, Special check
Disabled state¶
A GUI element with a disabled state does not react to touch.
See also
Element¶
An element is a basic interface component, either a self-contained high-level function or a object.
-
GUI library: Area, BarGraph, Button, CheckBox, Cursor, FlipFlop, Label, PlusMinus, RadioButtons, Text, TextBox, Table, Keyboard
-
Graphics library: Clock, Gauge, Histogram, Label, Multiple, Channels
The GUI elements react to touch, with two parameters: state, enabled or disabled; and mode, normal or instant.
See also
Enabled state¶
A GUI element with an enabled state reacts to touch and raises the corresponding event.
See also
Extension board¶
The extension board drives the e-paper display and provides other components like external SPI memory and I²C sensors.
It is connected
-
to the e-paper display through a 24- or 34-way flat cable; and
-
to the main controller board through a 2x10 or 1x10-way cable.
PDLS supports the EXT3, EXT3-1 and EXT3-Touch extension boards from Pervasive Displays.
The EXT3-Touch Expansion Board drives the I²C touch controller. It is placed below the EXT3-1.
See also
Fast update¶
The fast update is faster than the global update mode. First, the previous and next contents of the full screen are uploaded to the screen, and then the screen refreshes without the blinking effect.
It supports monochrome screens only, and possible ghosting may appear.
The fast update offers a good balance between quality and speed.
See also
File formats¶
There are multiple options to store and retrieve the content of the screen:
-
Image structure;
-
Portable bitmap or pixmap (with
PBMorP4extension); -
Windows bitmap (with
BMPextension); -
Portable Network Graphic (with
PNGextension) for the Viewer edition only.
See also
Frame-buffer¶
Compared to other screens, the e-paper screens relies on a frame-buffer.
-
First, the commands for drawing text and graphics update the frame-buffer.
-
Then, the update command sends the content of the frame-buffer to the screen and refreshes the panel.
The frame-buffer resides on either the internal MCU RAM or on an external SPI SRAM.
See also
Global update¶
The global update is the default for refreshing the screen. First, the next content of the full screen is uploaded to the screen, and then the screen refreshes with a blinking effect.
It supports both monochrome and colours screens. However, it is slower than the other modes.
The global update is recommended for optimal quality without any ghosting.
See also
Image structure¶
The image structure is a specific file format to store the content of the screen.
It is used to write to a micro-SD card or to print to a serial console, for later reuse as a header file.
It comes in two formats: image for monochrome displays; and 16-bit image for monochrome and colour displays.
See also
Instant check¶
Default mode is normal check mode.
In instant check mode, the GUI element raises the event when the finger touches the element. No cinematic sequence is performed.
It requires the state of the GUI element to be enabled.
See also
Direct check, Enabled state, Check mode, Normal check, Special check
Logical screen¶
The library deals with the logical screen, which takes into account the orientation, with x-y coordinates.
The coordinates for the logical screen are defined by the orientation.
See also
Main controller board¶
The main controller board can be powered by a microcontroller or a microprocessor. It runs the application based on PDLS.
It is connected to the extension board through GPIOs and the SPI and I²C bus.
A dedicated header file provides the list of the pre-configured main controller boards.
The four recommended boards are the Adafruit Feather nRF52840, the Arduino Nano Matter, the Espressif ESP32-DevKitC and the Raspberry Pi Pico RP2040.
An application note explains how to define a non-listed main controller board.
See also
Normal check¶
Default mode is normal check mode.
In normal check mode, the GUI element requires the finger to be hold for a moment and raises the event when the finger is released from the element. Additionally, the element goes through a cinematic sequence.
It requires the state of the GUI element to be enabled.
See also
Direct check, Enabled state, Check mode, Instant check, Special check
OTP memory¶
The OTP memory contains the parameters needed to drive the screen during refresh. OTP stands for one-time programming.
Those parameters are calibrated to ensure the optimal image quality. The library reads them once and use them to refresh the screen.
Page¶
A page is a set of elements that defines a screen of a human machine interface.
An application can have one single page or multiple pages.
See also
Partial update¶
Warning
The partial update mode is now deprecated and replaced by the fast update mode.
The partial update is the fastest among other update options. Instead of the full screen, only the previous and next contents of the modified window are uploaded to the screen, and then the screen refreshes without the blinking effect.
It supports monochrome screens only. Possible ghosting may appear, especially outside the modified window.
The partial update is highly recommended for human-machine interfaces.
See also
Physical screen¶
The physical screen refers to the panel as described in the data-sheet, with horizontal-vertical coordinates.
The coordinates for the physical screen are consistent with the horizontal and vertical axes from the data-sheet.
The library manages the physical screen and exposes the logical screen to the application.
See also
Portable pixmap¶
The portable pixmap is a compact file format with a PBM or P4 extension to store the content of the screen.
It is used to write to and read from a micro-SD card.
It is also available to print as a table to a serial console, for later reuse as a header file.
See also
Rectangular coordinates¶
The rectangle coordinates include two points P1 and P2.
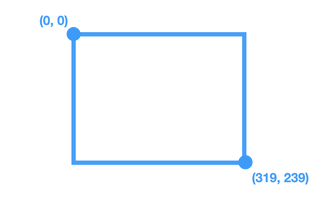
-
P1 is a pixel on the top left, with (
x1,y1) coordinates. -
P2 is a pixel on the bottom right, with (
x2,y2) coordinates.
Example
rectangle (0, 0) - (319, 239)
See also
Screen¶
A same screen is described as
-
a physical screen is the panel described in the data-sheet;
-
a logical screen is managed by the library and takes the orientation into account.
See also
Special check¶
Default mode is normal check mode.
In special check mode, the GUI element raises the event when the finger is released from the element. A simplified cinematic sequence is performed.
The mode is a simplified and faster variant of the normal check mode.
It requires the state of the GUI element to be enabled.
See also
Direct check, Enabled state, Check mode, Instant check, Normal check
State¶
The state of a GUI element defines whether the element reacts to touch.
Two states are available:
-
if state is disabled, the element does not react to touch;
-
if state is enabled, the element reacts to touch and raises the corresponding event.
See also
Update¶
Three modes are available for the update of the screen: global update, fast update, partial update.
Changing the content of the screen consists on three phases:
-
initialising the panel;
-
uploading the content of the frame-buffer to the panel; and
-
refreshing the panel.
| Update type | Global Update | Fast Update | Partial Update |
|---|---|---|---|
| Supported panels | Three-colours (BWR) and monochrome (B&W) panels | Monochrome (B&W) panels | Monochrome (B&W) panels |
| Initialisation | Panel initialisation | Panel initialisation | Panel initialisation |
| Content upload | Full screen with new content | Full screen with previous and new contents | Partial window with previous and new contents |
| Panel refresh | Whole screen with flashing effect | Whole screen with fast mode | Partial window with fast mode |
| Image quality | Optimal quality | Possible ghosting | Possible ghosting |
| Upload speed | Slow | Slow | Fast |
| Refresh panel speed | Slow | Fast | Fast |
| Overall speed | Slow | Faster | Fastest |
See also
Vector coordinates¶
The vector coordinates include one point P0 and one distance.
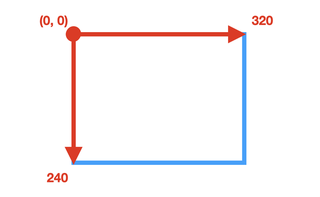
-
P0 is a pixel and the origin, with (
x0,y0) coordinates. -
The distance (
dx,dy) is specified on thex-yaxes.
Example
vector (0, 0) - (320, 240)
Going from pixel 0 to pixel 319 represents 320 pixels in total.
See also
Viewer¶
The Viewer edition runs as a Linux and Windows native application to simulate an e-paper screen and manage touch. It shares the same fonts and application libraries with the Commercial edition.
It allows to develop the application software independently of the hardware. It is meant to be used with the Commercial edition.
Window¶
The window is the area to be updated on partial mode.
The library calculates the window automatically.
See also
Windows bitmap¶
The Windows bitmap is a file format with a BMP extension to store the content of the screen.
It is used to write to and read from a micro-SD card.
See also